Introduction to BPEL
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) is a XML-based language used to define enterprise business processes within Web services.
Every company has its unique way of defining its business process flow.
The key objective of BPEL is to standardize the format of business process flow definition so companies can work together seamlessly using Web services. BPEL extends the Web services interaction model and enables it to support business transactions. BPEL is based on Web services in the sense that each of the business process involved is assumed to be implemented as a Web service. Processes written in BPEL can orchestrate interactions between Web services using XML documents in a standardized manner. These processes can be executed on any platform or product that complies with
the BPEL specification.
BPEL supports two different types of Business Processes:
- Executable processes: Models the actual behavior of a participant in a business interaction. They follow the orchestration paradigm and can be executed by an orchestration engine.
- Abstract processes: Uses process descriptions that specify the mutually visible message exchange behavior of each of the parties involved in the protocol, without revealing their internal behavior.
The History of BPEL
BPEL is a convergence of language features from IBM's Web Service Flow Language (WSFL) that uses a directed graph approach and Microsoft's XLANG, which is the orchestration language, used in BizTalk server and has a block-structured approach. Both WSFL and XLANG are now superseded by the BPEL specification.
BPEL 1.0 was jointly developed by IBM, BEA, SAP, Siebel, and Microsoft in August 2002. In April 2003, BPEL 1.1 was submitted to OASIS to obtain even broader industry acceptance and open standardization.
BPEL's Relation to other Web Service Standards
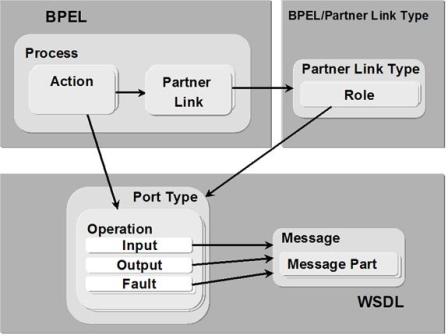
BPEL is based upon Web services and hence is related to standards such as WSDL, XML, SOAP, and UDDI. The following diagram describes the relations between the various standards within the Web services technology stack.

The BPEL process model is layered on top of the service model defined by WSDL. It is the notion of peer-to-peer interaction between services described in WSDL. A business process defines the interaction between a process instance and its partners.
To define business processes, BPEL describes a variety of XML elements, such as:
- Partners: The actors in a business transaction
- Containers: The messages that need to be transmitted
- Operations: The type of Web services that are required
- Port types: The kinds of Web services connections that are required for operations
BPEL Summary
- BPEL defines the business process flow in a standard manner and describes the process logic of invocation of the involved Web services.
- WSDL defines the interface details of the Web services.UDDI defines a standard for publishing and discovery of the Web service. SOAP defines the message level format for accessing the Web service.
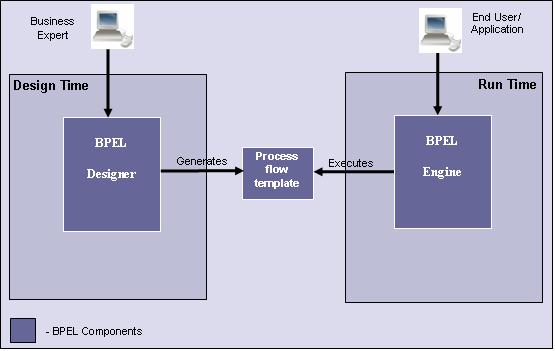
BPEL Components: Architecture
The three core components of BPEL are the:- BPEL Designer
- Process flow template
- BPEL Engine
In a typical BPEL scenario, a business expert/analyst of a company would use the BPEL Designer (a Graphical User Interface) and define
the business process. A business process, for example, could be a 'Purchase Order' business scenario. Web services needed for this scenario would be included in the flow that uses the designer. Once the business expert defines the business process flow, a process logic template containing the process flow logic would be generated by the Designer in the background. At runtime, this process template would be
executed by the BPEL Engine.
BPEL designer
A Graphical User Interface is used to define a business process that would be independent of the underlying applications. It is intuitive for the Business experts to define the process without being overly technical in depth.
It generates the BPEL process flow logic template.
It generates the BPEL process flow logic template.
Process flow template
The process flow format adheres to the BPEL specification. It captures the business process flow logic. It is generated from the BPEL
designer at design time and executed by the BPEL Engine at runtime. Following is a sample process flow template for a HelloWorld Web service invocation.

Note: The above process logic code is not a BPEL tool generated; therefore, it might vary in the actual syntax. The intention is to
introduce readers to the various XML elements in the BPEL.
BPEL Engine
Executes any process flow template compatible to the BPEL standard. Functionality includes invocation of the Web services, mapping of the
data content, error handling, transactionality, security, and so forth. Typically, the BPEL Engine would be integrated within the
Application Server.
BPEL Engines & Designer
The following table lists some of the various BPEL products available. Some of these companies have free trial versions available; others
allow you to download the product for free to use in conjunction with their other products. ActiveBPEL has an Open Source version of its
product.
| Products | Links |
|---|---|
| a) Active BPEL Designer b) Active BPEL Engine | Active-Endpoints Products |
| BPWS4J, WBI Server Foundation | IBM Developer
Software Integration (wbisf) |
| Oracle BPEL Process Manager | Oracle Technology BPEL |
| Parasoft BPEL Maestro | Parasoft SOA |
Conclusion
This article provided an overview of BPEL basics, the BPEL architecture, and some of the BPEL products available for developers to get
hands on. This article could be considered as a good starter for BPEL and not to be considered a BPEL reference/implementation
guide.The architecture explained in this article is more generic and no way specific to any BPEL product. I hope that, as more and more
reliable BPEL products would be available in the market, more companies will move their enterprise systems towards the BPEL standard for
their business processes.